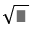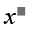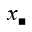-
Aomike 22/03/2017 at 21:03
Set x + 29 = t (*)
The given equation becomes: \(\dfrac{1}{t^2}+\dfrac{1}{\left(t+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(t+1\right)^2+t^2}{t^2\left(t+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{t^2+2t+1+t^2}{t^2\left(t^2+1+2t\right)}=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(t^2+2t+1+t^2\right)=5t^2\left(t^2+1+2t\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 8t2 + 8t + 4 = 5t4 + 5t2 + 10t3
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5t4 + 10t3 - 3t2 - 8t - 4 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5t4 - 5t3 + 15t3 - 15t2 + 12t2 - 12t + 4t - 4 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-1\right)\left(5t^3+15t^2+12t+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-1\right)\left(5t^3+10t^2+5t^2+10t+2t+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-1\right)\left(t+2\right)\left(5t^2+5t+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-1\right)\left(t+2\right).5.\left[\left(t+\dfrac{5}{4}\right)^2-\dfrac{93}{80}\right]=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t-1=0\\t+2=0\\\left(t+\dfrac{5}{4}\right)^2-\dfrac{93}{80}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\\t=-2\\\left(t+\dfrac{5}{4}\right)^2=\dfrac{93}{80}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\\t=-2\\t=\dfrac{-25+\sqrt{465}}{20}\\t=\dfrac{-25-\sqrt{465}}{20}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Now just replace (*) is ok
Run my EDM selected this answer.
-
An Duong 19/05/2017 at 17:20
Assume that 0 < a < b < c < d.
The greatest number m formed by using the four digits is \(\overline{dcba}\).
And the least number n formed by using the four digits is \(\overline{abcd}\).
We have: \(\overline{dcba}+\overline{abcd}=1330\)
since \(\overline{abcd}>1000\) and \(\overline{dcba}>1000\) => \(\overline{dcba}+\overline{abcd}>2000\).
Therefore, there is no a, b, c, d sastifies the problem.
-
WhySoSerious 16/08/2017 at 15:10
The list that 2, 0, 1 and 4 are used to create is :
1024 2014 4012 1042 2041 4021 1240 2104 4210 1204 2140 4201 1402 2401 4102 1420 2410 4120 The sum of all numbers is : 45108.
So the arithmetic mean of all these integers is \(\dfrac{45108}{16}=2506\)
Selected by MathYouLike
-
We have : \(x\le1\)\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2\le x\\\sqrt{x}\le1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2\le x\\x\le\sqrt{x}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}\ge x^2\)
\(\Rightarrow y\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{1}{4}\ge yx^2+\dfrac{1}{4}\) (the equality happens when x = 0 or x = 1)
Moreover, \(yx^2+\dfrac{1}{4}\ge2\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}yx^2}=x\sqrt{y}\)
(the equality happens only when \(yx^2=\dfrac{1}{4}\))
So, \(y\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{1}{4}\ge x\sqrt{y}\) or \(x\sqrt{y}-y\sqrt{x}\le\dfrac{1}{4}\)
The equality happens when : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\yx^2=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Selected by MathYouLike
-
B = (x2 + 1)(y2 + 1) - (x + 4)(x - 4) - (y - 5)(y + 5)
= x2y2 + x2 + y2 + 1 - x2 + 16 - y2 + 25
= x2y2 + 42 \(\ge42\forall x,y\)
The equality happens when :
\(xy=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0;y\ne0\\x\ne0;y=0\\x=y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Kaya Renger selected this answer.
-
Tell the commission of Mr. Jones and Mr. Smith is a and b
a = 3% widgets
b = 5% widgets
=> a/b = 3/5
=> The answer is: 500/5.3 = 300 widgets
-
Vũ Mạnh Hùng 03/12/2017 at 13:13
mr. jones make commission more than mr. smith:
5-3=2(%)
mr.smith sold
(500:2%)*3=750(widgets)
-
Mr Smith makes the commission more than Mr Jones: \(5\%-3\%=2\%\)
Mr Smith sold: \(\left(500:2\%\right)\cdot3\%=750\left(widgets\right)\)
-
Cristiano Ronaldo 03/08/2018 at 14:39
No fruit, no tree
But there are seeds falling out of place
The tree fell off happy
Animals find shelter to hide.
What is the quiz?Answer: It's a raindrops
Hello selected this answer.