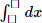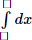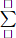Phan Minh Anh
10/06/2017 at 16:20
-
Phan Minh Anh 14/06/2017 at 12:58
It Thai Son mountain.
-
Đỗ Thanh Hải 29/06/2017 at 09:51
Núi Thái Sơn nha Bạn
-
Phan Minh Anh 10/06/2017 at 16:21
Sorry: What the mountains cut into pieces?
-
FA KAKALOTS 28/01/2018 at 22:08
For any natural number n > 1,we have :
(n - 1)n(n + 1) = n(n2 - 1) = n3 - n < n3
⇒1n3<1(n−1)n(n+1)
1(n−1)n(n+1)=1n.1(n−1)(n+1)
=1n.(n+1)−(n−1)(n−1)(n+1).12=12.1n.(1n−1−1n+1)
=12.(1(n−1)n−1n(n+1))
Now we have :
E < 12.3.4+13.4.5+14.5.6+...+1(n−1)n(n+1)
=12(12.3−13.4)+12(13.4−14.5)+12(14.5−15.6)+...+12(1(n−1)n−1n(n+1))
=12(12.3−1n(n+1))=112−12n(n+1)<112
Hence,E<112
-
For any natural number n > 1,we have :
(n - 1)n(n + 1) = n(n2 - 1) = n3 - n < n3
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{n^3}< \dfrac{1}{\left(n-1\right)n\left(n+1\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{\left(n-1\right)n\left(n+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{n}.\dfrac{1}{\left(n-1\right)\left(n+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{n}.\dfrac{\left(n+1\right)-\left(n-1\right)}{\left(n-1\right)\left(n+1\right)}.\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{n}.\left(\dfrac{1}{n-1}-\dfrac{1}{n+1}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}.\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(n-1\right)n}-\dfrac{1}{n\left(n+1\right)}\right)\)
Now we have :
E < \(\dfrac{1}{2.3.4}+\dfrac{1}{3.4.5}+\dfrac{1}{4.5.6}+...+\dfrac{1}{\left(n-1\right)n\left(n+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{2.3}-\dfrac{1}{3.4}\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{3.4}-\dfrac{1}{4.5}\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{4.5}-\dfrac{1}{5.6}\right)+...+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(n-1\right)n}-\dfrac{1}{n\left(n+1\right)}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{2.3}-\dfrac{1}{n\left(n+1\right)}\right)=\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{2n\left(n+1\right)}< \dfrac{1}{12}\)
Hence,\(E< \dfrac{1}{12}\)
-
FA Liên Quân Garena 08/01/2018 at 21:09
We have :
\(=\dfrac{\left(x^3+x^2\right)-\left(x+1\right)}{x^2-5x-x+5}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)-5\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x-5}\)
HỦY DIỆT THE WORLD selected this answer.
-
Thao Dola 14/03/2017 at 14:23
The first such triple is 8 = \(2^2+2^2\),9 = \(3^3+0^2\),10=\(3^2+1^2\), which suggests we consider triples \(x^2-1,x^2,x^2+1\).Since \(x^2-2y^2=1\) has infinitely many positive solutions (x,y), we see that \(x^2-1=y^2+y^2,x^2=x^2+0^2\)and \(x^2+1\) satisfy the requiment and there are infinitely many such triples.
Selected by MathYouLike -
FA KAKALOTS 28/01/2018 at 22:12
The first such triple is 8 = 22+22,9 = 33+02,10=32+12, which suggests we consider triples x2−1,x2,x2+1.Since x2−2y2=1 has infinitely many positive solutions (x,y), we see that x2−1=y2+y2,x2=x2+02and x2+1 satisfy the requiment and there are infinitely many such triples.
-
Such doge 14/03/2017 at 21:03
Wowe it hard
-
a.
\(x^2-2y^2=xy\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2y^2-xy=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-y^2\right)-\left(y^2+xy\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)-y\left(x+y\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y-y\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)\left(x-2y\right)=0\)
But \(x+y\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2y=0\Leftrightarrow x=2y\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\dfrac{x-y}{x+y}=\dfrac{2y-y}{2y+y}=\dfrac{y}{3y}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
-
Alone 31/12/2017 at 11:19
Continue Dao Trong Luan'answer:
\(\left(x-1\right)\left[x^2-4\left(x-1\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)^2\)
FA Liên Quân Garena selected this answer. -
FA Liên Quân Garena 01/01/2018 at 10:26
I edited the subject
x3−x2−4x2+8x−4
=x2(x−1)−(4x2−8x+4)
=x2(x−1)−[(2x)2−2⋅2x⋅2+22]
=x2(x−1)−(2x−2)2
=x2(x−1)−4(x−1)2
=(x−1)[x2−4(x−1)]
(x−1)[x2−4(x−1)]
=(x−1)(x2−4x+4)
=(x−1)(x−2)2
-
Hương Yêu Dấu 31/12/2017 at 13:33
We have :
(x - 1) . [x2 - 4 . (x - 1)]
<=> (x - 1) . (x2 - 4x + 4)
=> (x - 1). (x - 2)2
This is brief
-
Alone 31/12/2017 at 11:07
We have:\(\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3-\left(x^2-25\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3-x^3+2x^2+25x-50=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-x^3+23x-53=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(3-x\right)-23\left(3-x\right)+16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-23\right)\left(3-x\right)+16=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-23\in\left\{-16,-8,-4,-2,-1,1,2,4,8,16\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2\in\left\{7,15,19,21,22,24,25,27,31,39\right\}\)
Because 3-x is a integer number so x is a integer number so \(x^2=25\) and 3-x=-8
\(\Rightarrow\) x=\(\pm\)5 and x=11 (unsatisfactory)
So not have x satisfy
FA Liên Quân Garena selected this answer.
-
Lightning Farron 30/12/2017 at 23:44
Stop Touching YourSelf, please =((
-
Ngu Ngu Ngu 13/04/2017 at 22:55
Put the equation above is \(\left(1\right)\)
If \(xy>0\) then:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{17}{y}+\dfrac{2}{x}=2011\\\dfrac{1}{y}-\dfrac{2}{x}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1007}{9}\\\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{490}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{9}{490}\\y=\dfrac{9}{1007}\end{matrix}\right.\) (satisfy)
If \(xy< 0\) then:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{17}{y}+\dfrac{2}{x}=-2011\\\dfrac{1}{y}-\dfrac{2}{x}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{y}=-\dfrac{1004}{9}\\\dfrac{1}{x}=-\dfrac{1031}{18}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow xy>0\) (unsatisfactory)
If \(xy=0\) then: \(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x=y=0\) (satisfy)
Conclude: equations have 2 solutions: \(\left(0;0\right)\) and \(\left(\dfrac{9}{490};\dfrac{9}{1007}\right)\)
Nguyễn Thị Huyền Mai selected this answer.
-
Ngu Ngu Ngu 14/04/2017 at 08:08
\(2\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)+3\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)-16=0\left(1\right)\)
Condition: \(x\ne0\)
Put \(t=x+\dfrac{1}{x}\Rightarrow x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}=t^2-2\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow2t^2+3t-20=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-4\\t=\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
If \(t=-4\Rightarrow x=-2\pm\sqrt{3}\)
If \(t=\dfrac{5}{2}\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Conclude:...
Use Ka Ti selected this answer.